New Delhi — Researchers at the National Institute of Technology (NIT) Rourkela have pioneered an environmentally safe method to fight antimicrobial resistance by using extracts from medicinal plants to produce powerful antibacterial agents.
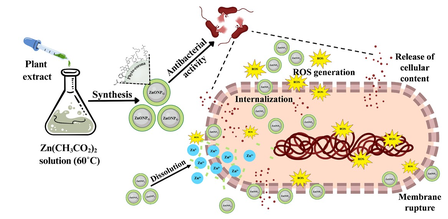
The overuse of conventional antibiotics has fueled the rise of “superbugs” that are increasingly resistant to existing treatments. To address this, the NIT team employed an eco-friendly approach to synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles, known for their ability to disrupt bacterial cells.
Instead of harsh chemicals, the researchers used leaf and petal extracts from Marigold, Mango, and Eucalyptus to reduce zinc salts into zinc oxide nanocrystals coated with plant-derived compounds. Nanoparticles coated with marigold extracts were found to be twice as effective in killing bacteria compared to chemically synthesized nanoparticles or plant extracts alone.
The plant extracts not only facilitated the nanoparticle synthesis but also stabilized them by forming a herbal “phytocorona,” which controls the release of zinc ions and ensures sustained antibacterial action. Flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins, and phenolic compounds in the extracts provide inherent antibacterial properties, resulting in a dual mechanism to combat bacterial growth.
“The green-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles with phyto-corona represent a sustainable and effective antimicrobial platform. They leverage medicinal plant compounds to provide a potent solution against antimicrobial resistance,” said Prof. Suman Jha, Associate Professor at NIT Rourkela’s Department of Life Science.
Using indigenous plant extracts makes the technology scalable and promotes home-grown, sustainable solutions, reducing dependence on imported drugs and synthetic antibiotics.
“Our goal is to develop scalable, affordable, and eco-friendly antimicrobial materials for use in healthcare, sanitation, and food preservation. By harnessing India’s biodiversity, we aim to create self-reliant innovations that advance global health and sustainability,” Jha added.
With inputs from IANS